A bond is a type of financial instrument. Bonds are debt that firms and governments can issue to raise money and they earn interest.
Characteristics of Bonds

1. Inverse Relationship
There is an inverse relationship between the price of a bond and the market interest rate. Bonds have a resale (or secondary) market. A bond’s secondary market value is it’s Present Discount Value = Face Value/(1+i)n
2. Interest Rate Risk
Bonds have interest rate risk. The longer the term of the bond, the higher the interest rate risk.
3. Yield to Maturity
Yield to Maturity is the effective interest rate as determined by the bond’s future payment schedule and its price. If it is based on the market interest rate, the bond sells for less than PDV, (i.e. bond is a bargain), then yield to maturity > i
Types of Bonds

1. Coupon Bonds
Coupon Bonds sell at or near face value (at par).
Example of a coupon bond:
Ex: $1000 coupon bond sells at approximately $1000

Coupon rate = Dollar value of yearly coupon payments/face value of the bond
Ex: $1000 face value, coupon bond that pays 5% coupon rate will make annual coupon payments of $50.
2. Discount Bonds (zero-coupon bonds)
They sell at less than face value; they pay no interest or coupons until the bond matures. The U.S. savings bond is a discount bond.
Price, Pd & Interest, interestd are jointly determined.
Interest = [(Face value of a bond/ Present Discount Value)^(1/N) – 1] * 100
Example of a Discount Bond
Ex: 1 year $1000 discount bond
id = [(Face value of a bond/ Pd)1/N – 1] * 100
Sells for $900
id = [(1000/9000)1 – 1] * 100 = 11.1%
Ex: Same as above except 2 year bond
id = [(1000/900)0.5 – 1] * 100 = 5.4%
Pd = face value/ (1 + id)n = PDV
Present Discount Value (PDV) = C (coupon payment) / (1 + i) + C / (1 + i)2 + C / (1 + i)3 + …. + C (coupon payment) / (1 + i)N + Face Value/ (1 + i)n
Ex: PDV of 2 year coupon bond, face value = $1000
Coupon payment = $50
Coupon rate – 5%
PDV = 50/(1+0.05) + 50/(1+0.05)2 + 1000/(1 + 0.05)2 = $1000
Face Value = PDV as long as coupon rate = market interest rate
3. A Consol
A counsol is a type of coupon that pays forever but never pays the principal.
PDV of fixed payment in perpetuity = Fixed Income / i
Example of a Consol
Ex: C = $50 forever
i =5%
PDV = 50/0.05 = $1000
Inverse Relationship
Ex: 1 year, $1000 face value discount bond
id Pd
0% 1000/(1 + 0) = $1000
1% 1000/(1 + 0.01) = $990.10
5% 1000/(1 + 0.05) = $952.38
10% 1000/ (1 + 0.1) = $909.09
100% 1000/ (1 + 1) = $500
The Bond Price Interest Relationship
If interest goes up:
Discount Bonds (New): Pd goes down
Discount Bonds (Old): Pd falls (resale market)
Coupon Bonds (New): price unchanged (coupon rate changes) but if coupon rate is lower, then price falls
Coupon Bonds (Old): Pd falls (resale market)
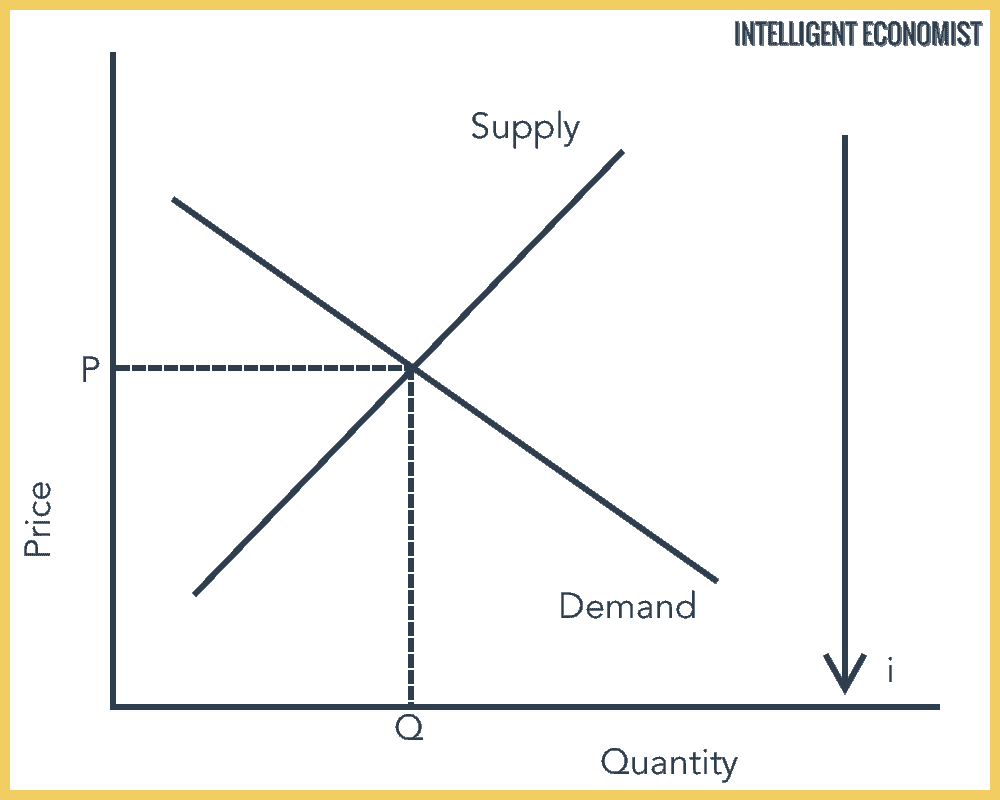
Demand And Supply in Bond Markets
With the third axis, this is known as the Loanable Funds Framework
ib = {(Face Value/Pd)1/N – 1} X 100
ib and Pb are inversely related