The term “inferior good” describes a good for which demand decrease as incomes increase. They are the opposite of “normal goods,” which are goods for which demand increases as incomes increase (e.g. organic food, cars, or name-brand products).
Inferior and normal goods are in a relationship with one another—in other words, inferior goods exist when demand for alternatives to a particular good (normal goods) increases with increased income.
In the event of a recession, as incomes fall pretty much across the board, demand for inferior goods increases (and demand for normal goods decreases). Likewise, when the economy is stronger, the demand for inferior goods decreases (and demand for normal goods increases).
See this table for a clear explanation of the relationship between income increase/decrease and demand for both inferior and normal goods.
Relation between Income and Demand
| Income | Increase | Decrease |
|---|---|---|
| Demand for inferior goods | Decrease | Increase |
| Demand for normal goods | Increase | Decrease |
What is an Inferior Good?
“Inferior” in this context doesn’t automatically mean low-quality, although this is a reasonable assumption to make based on the term. Inferior goods can be of high or low quality, although they tend to often be lower quality and cheaper.
Due to their low price, they tend to be consumed by people with lower incomes. As their incomes increase, they tend to shift to more expensive alternatives.
Why Inferior Goods Matter
During recessions, there’s a surge in demand for such items as income levels fall. Inferior goods tend to be recession-proof. There were only two stocks in the Dow Jones Industrial Average that increased in value in 2008. This was during the 2007-2008 financial crisis, arguably “the worst economic disaster since the Great Depression of 1929.”
Can you guess which two stocks thrived?
McDonalds and Walmart. Both companies position themselves as cost options.
Examples of Inferior Good
Here are some examples of inferior goods.
- Canned vegetables: People with lower incomes tend to rely on canned vegetables. Canned vegetables tend to be cheaper than fresh vegetables. Those who make more money are more likely to pay more for fresh vegetables.
- Fast food: When people make less money, they often choose fast food. When they make more money, they tend to eat at more expensive restaurants.
- Public transportation: When people make more money, their demand for cars/taxis (the normal good in this situation) increases.
- Cheap motels: Those who can afford to stay at a more expensive hotel with more attentive service, more comfortable beds, etc.
- Generic and store brands: When people have less money, they choose generic/store brands, as these are typically much cheaper. With more money, they often choose the normal good of name-brand products.
Demand For An Inferior Good Graph
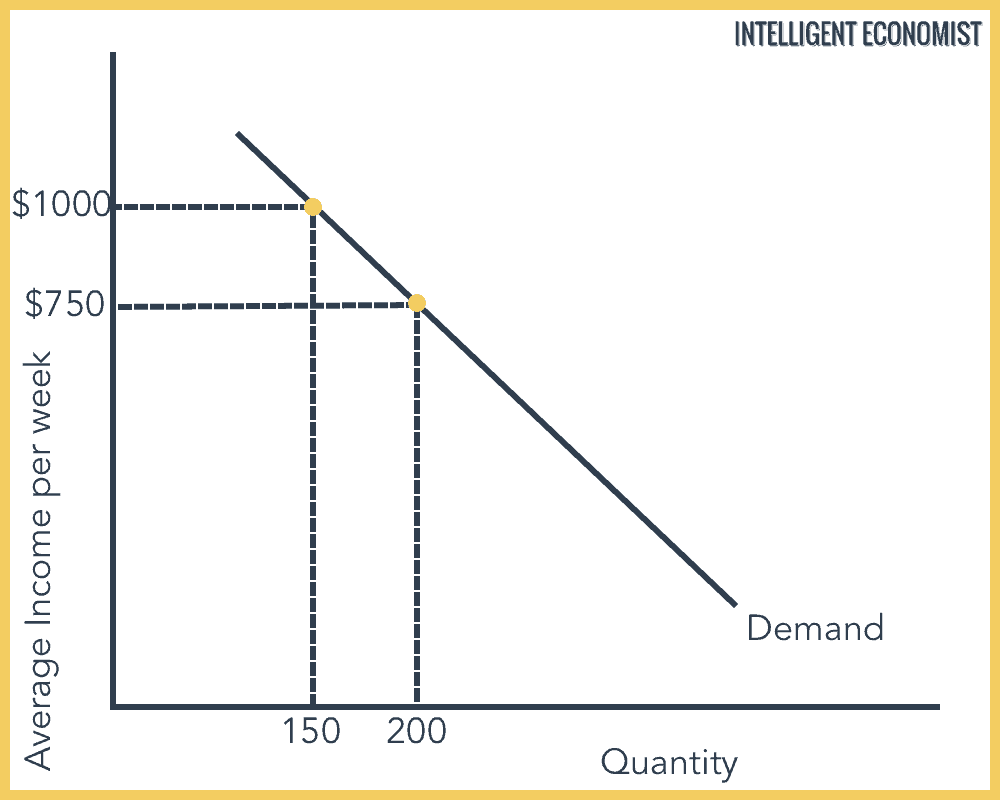
In the graph shown above, as average income per week increases from $750 to $1000, the demand for the inferior good, for example, cheap motels, decreases from 200 to 150 units.
Relationship with Income Elasticity of Demand (YED)
Income elasticity of demand describes the degree to which demand responds to changes in income (increases or decreases). It demonstrates whether a good should be considered a luxury or basic need. It is calculated as follows:
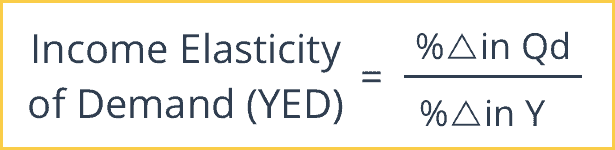
Income elasticity of demand (YED) = % change in demand ÷ % change in income
The income elasticity of demand for an inferior good is negative. Conversely, normal goods’ income elasticity of demand is positive.


I have a question that why would one consume less of inferior goods?