The result of the interaction between consumers and producers in a competitive market determines Supply and Demand equilibrium, price and quantity.
Market forces tend to drop the price if the quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded and prices rise if quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied. This movement continues until there are no more changes, and quantity demanded equals quantity supplied. This result is market equilibrium.
Supply and Demand Equilibrium
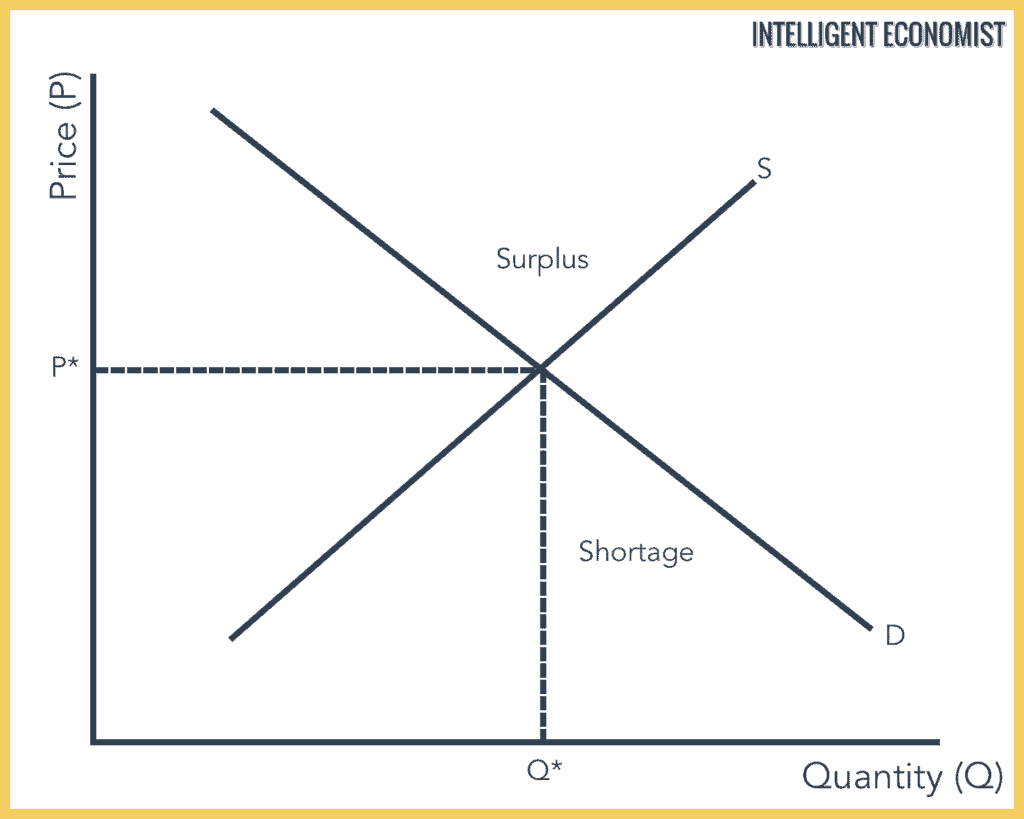
In the diagram below, you can see the Supply and Demand equilibrium with equilibrium price and quantity.
- P* is the equilibrium price
- Q* is the equilibrium quantity
Why is the Equilibrium Specifically at Price P* and Quantity Q*?
At a higher price, there would be more quantity supplied than demanded so the seller would have to lower his price to sell his goods. If the sellers raise their price too high, where the demand is less than what they have to offer, then they will have a surplus that will force them to lower their price until they can sell their entire supply
At a lower price, there would be more quantity demanded than supplied so the buyer would have to spend more to buy goods. If the sellers set their prices too low, then they will sell their entire supply before they can satisfy the demands of the market. This would result in a shortage in the market.
How An Increase in Demand Affects Market Equilibrium
We will now look at how changes in Supply and Demand affect the equilibrium. We will note the changes in equilibrium price and quantity.
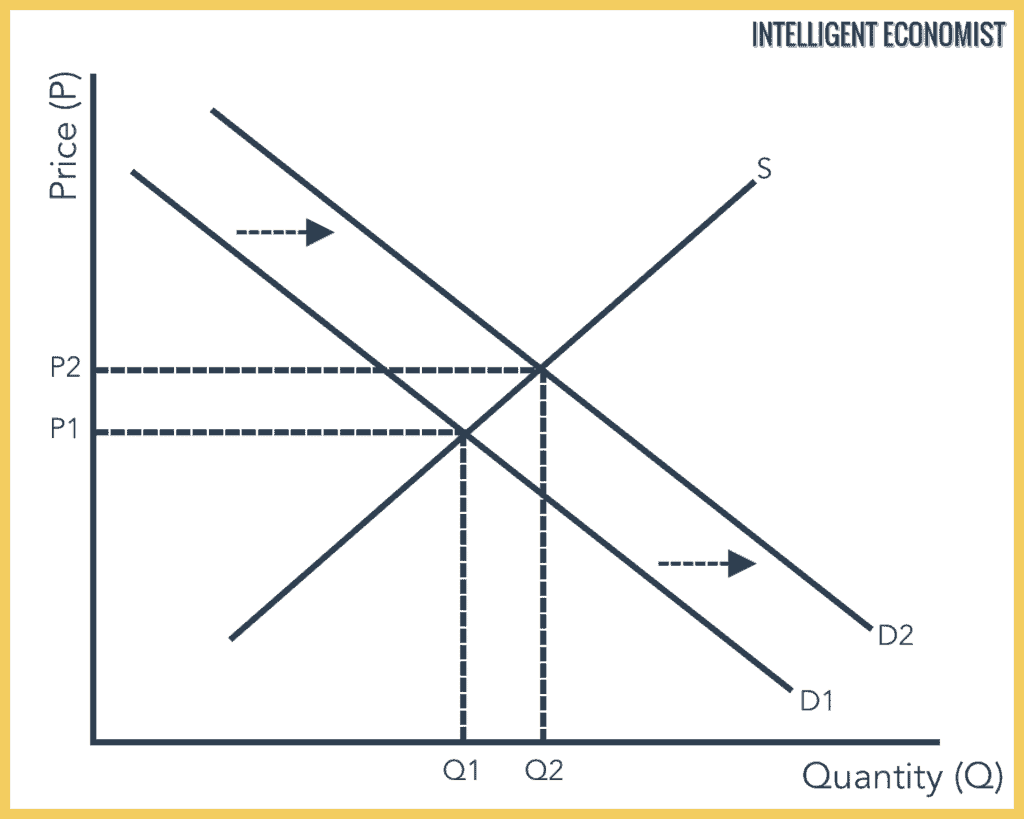
In the above graph, we see an increase or upward shift in the demand curve from D1 to D2. This increase can be because of some factors. The result of this increase in demand while supply remains constant is that the Supply and Demand equilibrium shifts from price P1 to P2, and quantity demanded and supplied increases from Q1 to Q2.
How A Decrease in Demand Affects Market Equilibrium
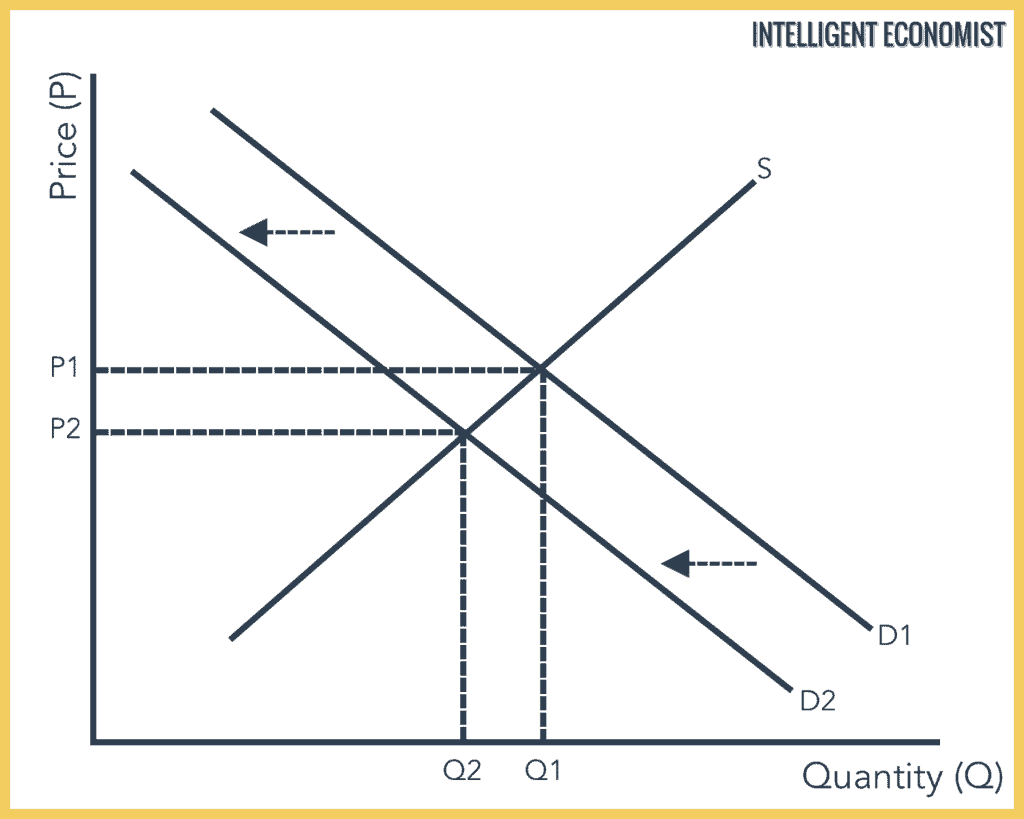
In the below graph, we see a decrease or downward shift in the demand curve from D1 to D2. This decrease can be because of some factors that affect demand. The result of this decrease in demand while supply remains constant is that the equilibrium falls from price P1 to P2, and quantity demanded and supplied decreases from Q1 to Q2.
How An Increase in Supply Affects Market Equilibrium
In the below graph, we see an increase or upward shift in the supply curve from S1 to S2. This increase can occur because of a number of factors. The result of this increase in supply while demand remains constant is that the Supply and Demand equilibrium shifts from price P1 to P2, and quantity demanded and supplied increases from Q1 to Q2.
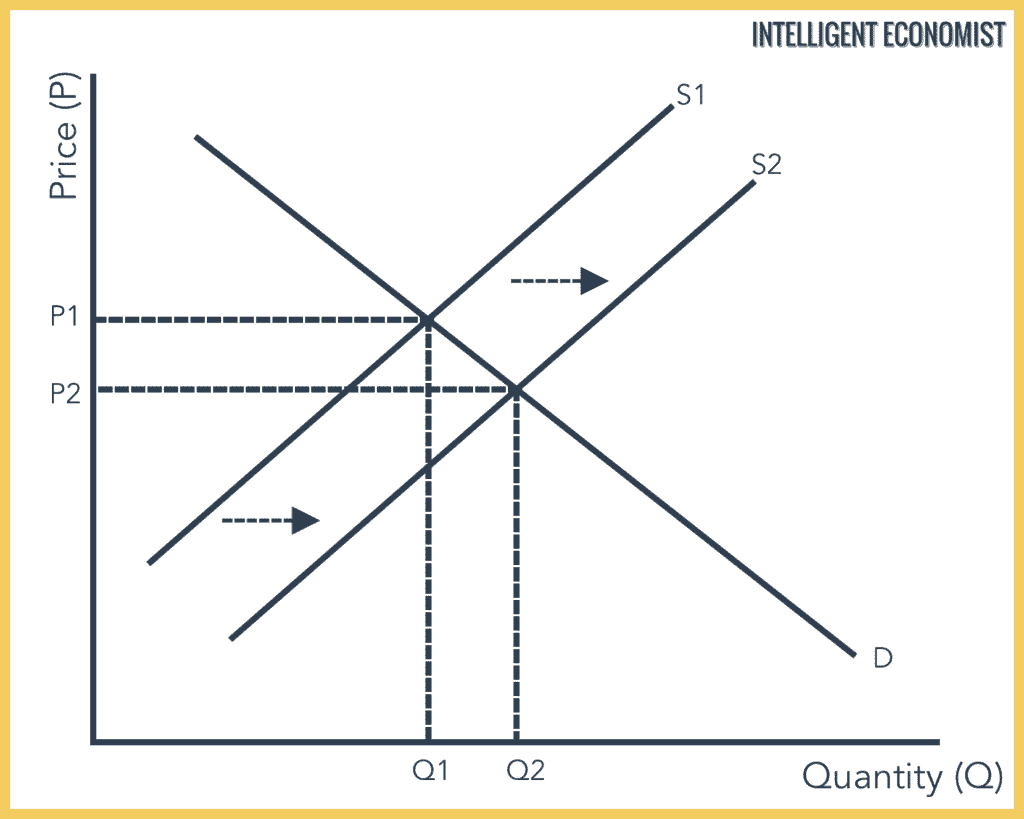
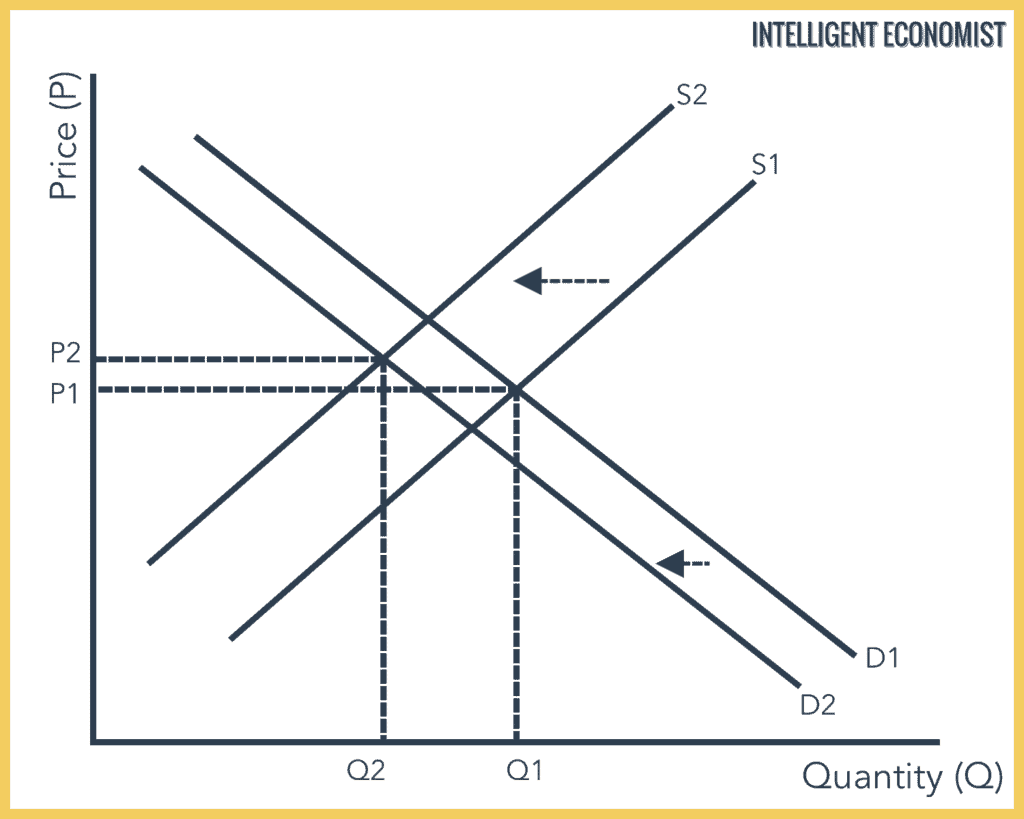
How A Decrease in Supply Affects Market Equilibrium
In the below graph, we see a decrease or downward shift in the supply curve from S1 to s2. This decrease can be because of a number of factors that affect supply. The result of this decrease in supply while demand remains constant is that the equilibrium falls from price P1 to P2, and quantity demanded and supplied decreases from Q1 to Q2.
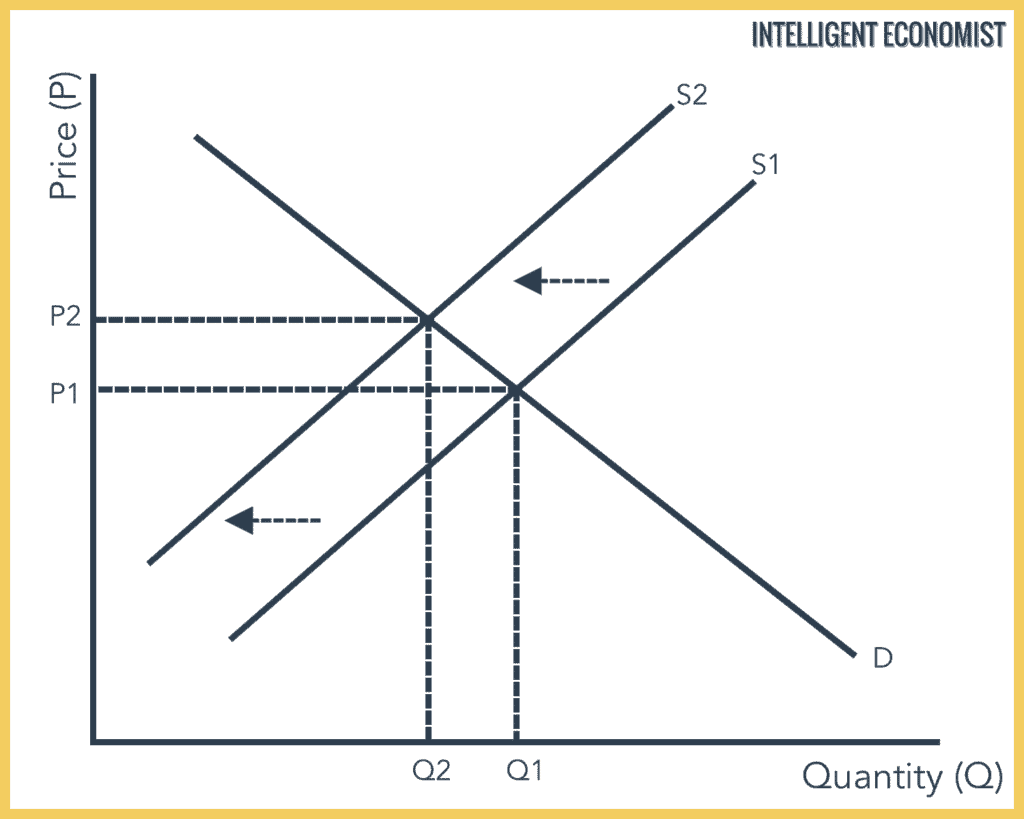
What Happens When There is a Decrease in Supply and Demand?
In this graph, both S & D fall from D1 to D2 and S1 to S2 respectively. The result is price increasing from P1 to P2 and quantity demanded and supplied decreasing from Q1 to Q2.